
AI Post Transformers
Failed to add items
Sorry, we are unable to add the item because your shopping basket is already at capacity.
Add to cart failed.
Please try again later
Add to wishlist failed.
Please try again later
Remove from wishlist failed.
Please try again later
Follow podcast failed
Unfollow podcast failed
-
Narrated by:
-
Written by:
-
mcgrof
About this listen
Episodes
-
 Less than 1 minute
Less than 1 minuteFailed to add items
Sorry, we are unable to add the item because your shopping basket is already at capacity.Add to cart failed.
Please try again laterAdd to wishlist failed.
Please try again laterRemove from wishlist failed.
Please try again laterFollow podcast failed
Unfollow podcast failed
-
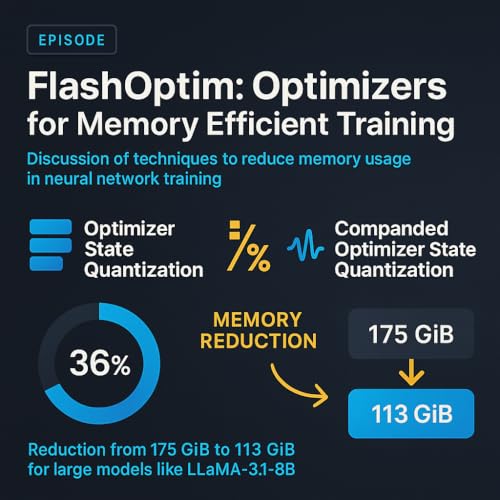 Less than 1 minute
Less than 1 minuteFailed to add items
Sorry, we are unable to add the item because your shopping basket is already at capacity.Add to cart failed.
Please try again laterAdd to wishlist failed.
Please try again laterRemove from wishlist failed.
Please try again laterFollow podcast failed
Unfollow podcast failed
-
 Less than 1 minute
Less than 1 minuteFailed to add items
Sorry, we are unable to add the item because your shopping basket is already at capacity.Add to cart failed.
Please try again laterAdd to wishlist failed.
Please try again laterRemove from wishlist failed.
Please try again laterFollow podcast failed
Unfollow podcast failed
No reviews yet


